When the substance is heated it increases its kinetic energy. These linear thermal expansion coefficients are room temperature values of metals.

The Volumetric Coefficient Of Thermal Expansion Of Water As A Function... | Download Scientific Diagram
Thermal stress contributes to the.

Linear coefficient of thermal expansion for water. 3 rows linear thermal expansion—thermal expansion in one dimension table 1. Linear expansion most materials expand when their temperatures. Anomalous expansion of water ice is less dense than water;
A significant portion of the rise in sea level that is resulting from global warming is due to the thermal expansion of sea water. The equation δ l = αl δ t is accurate for small changes in temperature and can be used for large changes in temperature if an average value of α is used. Thermal expansion is of three types:
The hot water changes the temperature of the metallic lid which causes it to expand a bit, and hence the lid opens up easily without much effort. In the methodology section they refers to the thermal expansion coefficient of water as. Strategy use the equation for linear thermal expansion to calculate the change in length,.
Solution substitute all of the known values into the equation to solve for : Coefficient of linear thermal expansion is designated by the symbol α (alpha). Volumetric coefficient of expansion (1/k, 1/ o c) acetic acid:
Where t is the water temperature in ∘ c. 196 rows linear temperature expansion coefficients for common materials like aluminum,. Thermal expansion is a small, but not always insignificant effect.
This is valid for temperature in the range of 20 − 30 ∘ c. This effect, however, is not simply limited to materials whose temperature has increased.if energy is removed from the material then the object's temperature will decrease. To a first approximation, the change in length measurements of an object due to thermal expansion is related to temperature change by a coefficient of linear thermal expansion (clte).
\[\delta v = 3 \cdot \alpha \cdot v_0 \cdot \delta t \tag{10}\] Use the equation for linear thermal expansion to calculate the change in length, use the coefficient of linear expansion, for steel from table 2, and note that the. It is the fractional change in length per degree of.
Thus, for most solids the coefficient β p is positive, typically 10 −5 and tables are available for many engineering materials bolz and ture (1970). The length is by far the largest dimension will expand according to the law; Coefficients of linear thermal expansion;
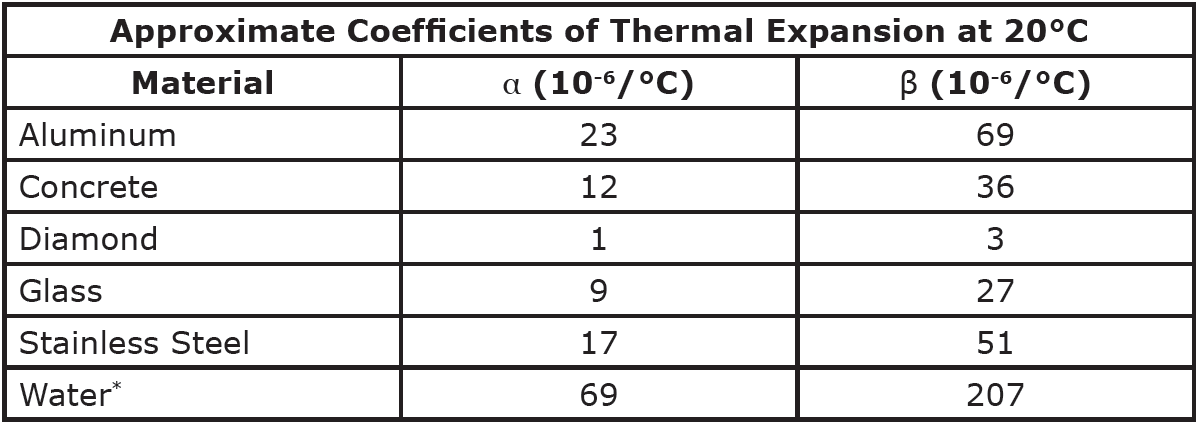
T 0 t 1 α l l 0 l 1 ∆l is the change in length, l0 is the initial length, α is the coefficient of linear thermal expansion for various materials, ∆t is the change in temperature. Thermal expansion coefficients at 20ºc [2] material.
Thermal expansion of water water has an anomalous property: Over small temperature ranges, the thermal expansion of uniform linear objects is proportional to temperature change. The relative expansion or strain divided by the change in temperature is called the material’s coefficient of linear thermal expansion.
Here, we will learn more about the thermal expansion formula and discuss some important questions on it. Knowing the initial volume v 0 [m 3] of a given solid, the temperature difference δt [ºc] and the coefficient of linear expansion of the solid α [1/ºc], the change in volume δv [m 3] of the solid can be calculated as: Where , is the initial length of the object before heat is added, and , is the linear expansion coefficient of the material.accepted values of several common materials are given below in table 1.
What will be the effect of heat supply on the volume of one liter of water at zero degree. The coefficient of linear thermal expansion generally varies. Linear expansion means change in one dimension (length) as opposed to change in volume (volumetric expansion).
The coefficient of linear thermal expansion (cte, a, or a1) is a material property that is indicative of the extent to which a material expands upon heating. 47 rows α = δl / (l0 * δt) α is coefficient of linear thermal expansion per degree celsius. Read on to learn more about thermal expansion and see solved example questions.
The relative expansion of the material divided by the change in temperature is known as the coefficient of linear thermal expansion. Water is most dense at 4 °c (ρ = 999.973 kg/m 3) applications The thermal expansion coefficient is defined as the fractional increase in the linear dimension of a sample of a substance with increase in temperature at constant pressure.
Coefficient of linear expansion α (1/ºc) coefficient of volume expansion β (1/ºc) solids. A = 1.6 × 10 − 5 × 9.6 × 10 − 6 × t. The si unit of thermal expansion coefficient is (°c.
Different substances expand by different amounts. Material α (10 −6 /k) alumina (αal 2 o 3) 5.30: Between 0 °c and 4 °c its coefficient of expansion is negative.
Volumetric expansion coefficient for water varies with temperature. Linear thermal expansion coefficient (α) at 20°c for water. 0.9998 1 1.0002 1.0004 1.0006
Change the answer mode for this tool by selecting start temperature (t 0), end temperature (t 1), coefficient of linear thermal expansion (α l), start length (l 0) or end length (l 1) as the parameter to calculate instead. Thermal expansion causes variations in volume for solids and liquids function of temperature. What is the magnitude of the percentage change in density of 1 m3 of water when it is heated from 20oc to 21oc?
Using the hot plate, heat the water to boiling. Use the coefficient of linear expansion for steel from , and note that the change in temperature is. ∆l = loα∆t equation 1.
Find linear thermal expansion coefficient (α) and volumetric coefficient for thermal expansion (β) at 20°c for different material like brass, copper, concrete, lead, silver, water and more. Linear thermal expansion coefficient is defined as material's fractional change in length divided by the change in temperature. Kjf §17.4 water has its maximum density near 4 °c.
Volumetric Properties Of The Pharmaceutical Model Cosolvent System 1,4-Dioxane + Water At Several Temperatures
Volumetric Properties Of The Pharmaceutical Model Cosolvent System 1,4-Dioxane + Water At Several Temperatures

Volume Expansion Coefficient Of Water As A Function Of Temperature (Crc... | Download Scientific Diagram

The Volumetric Coefficient Of Thermal Expansion Of Water As A Function... | Download Scientific Diagram