Joule’s law of heating was first published in 1840, as an abstract in the proceedings of the royal society, by james prescott joule.the law suggested that heat could be generated by passing an electric current through a wire. At the same time in history other workers were concerned with a study of the relationships existing between work done on a system and the mechanical energies of the system.

A) Temperature Distributions By Joule Heating Under Different Strain... | Download Scientific Diagram
Ohm s law v=i.r power law p=v.i 1.heat generated/dissipated due to energy flow h=i^2r.t (in case of a heating element,incandescent bulb )resistance is constant but heat produced is according to the material of the wire 2.increase in.
Joule hating temperature vs voltage. The unit of heat (either calorie or british thermal unit) was defined in terms of the rise in temperature produced when heat flowed into unit mass of water. The power, w = i^2 x r. Pure water is a terrible electrical conductor.
Record all data in the data table. Joule heating setup two boundary conditions. Measure and record the temperature t, the current i, and the voltage v every 60 s for 8 minutes.
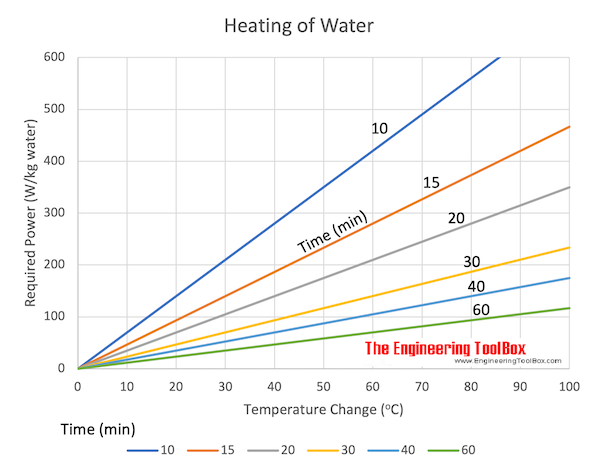
Calculate the dissipated power, p: Joule heating, often referred to as ohmic heating, heats water using electricity by passing electrical current directly through the water. May 16, 2015 at 18:02.
This research article focuses on the joule heating effect on a single resistor component miniature in size made up of copper. Joule’s law states that h (heat) = i (current) x v (voltage) x t (time the current is allowed to flow). Q = i 2 r t.
I = intensity of the circulating current expressed in amperes (a) r = electrical resistance of the conductor expressed in ohms. A complete model and numerical analysis of electroosmotic flow in a full capillary with the joule heating effect and the thermal end effects are presented in this section. From this study, he developed joule's laws of heating, the first of which is commonly referred to as the joule effect.joule's first law expresses the relationship between heat generated in a conductor and current flow, resistance, and time.
When a current flows through a material, it produces heat in it. As some dissimilar metal to metal junction was heated in your setup, it started to generate a small voltage difference somewhat proportional to the temperature difference. So, after a period of time t (sec) i can work out the temperature of the wire thus:
But there are materials whose resistance will change with voltage even in fixed temperature. R = the resistance in the conductor or circuit between the same two points, measured in ohms; H = i2 x r.
Next use the voltage, v, and the resistance to compute the current, i: A the output curves with various v g, and the inset is a narrow v ds range showing ohmic characteristics. Proportional to the square of the current i.e.
One can see joule heating as a transformation between “electrical energy” and “thermal energy. In interface science and technology, 2004. It is considered to be a major source of inaccuracy in major devices.
Joule heating is the physical effect by which the pass of current through an electrical conductor produces thermal energy. Let the timer run continuously and stir the system often. V (voltage) = i (current) x r (resistance), so the two equations are.
(1) the energy expended or heat generated in joules when a current of i amperes flows through a resistance of r ohms for t seconds is given as. H = i 2 r t joules. Joule immersed a length of wire in a fixed mass of water and measured the temperature rise due to a known current flowing through the wire for.
V = i x r. Practically, resistance typically does not change. Hence the electrons gain energy at the rate of vi per second.
Amount of heat (energy) delivered to something. Q = heat produced in joules (j) produced by the current. Between 1840 and 1843, joule carefully studied the heat produced by an electric current.
Area, a, and the resistivity, r: Also known as resistance heating, this function simulates heating due to electrical resistance. The consideration of the temperature dependent liquid properties couples the flow field, the electric potential field and the temperature field.
Using the heat transfer equation in. Joule heating is the generation of heat by passing an electric current through a metal. The primary inputs are current, voltage, and the material resistivity.
B the absolute value of the transfer curves with various v ds for ‘as fabricated’ and ‘al 2 o 3 passivated’ devices. Not really the reverse of the joule heating though. From the previous definition, the formula of joule's law can be expressed as follows:
This thermal energy is then evidenced through a rise in the conductor material temperature, thus the term “heating”. In this simplified joules law: The above expression is known as joule’s law, which states that the amount of heat produced in an electric circuit is.
Calculate the quantity mc, where mc = m wc w + m cc c and record it in the calculations table. When a voltage v is applied between the ends of the conductor, resulting in the flow of current i, the free electrons are accelerated. Now let's look not just at electrical resistance but at the heat generated when we change the resistance value or r or ohms.
T = time, in seconds (s) R = v / i. Or, written differently, h (heat) = i2 (current squared) x r (resistance) x t (time the current is allowed to flow).
The voltage v in the data table. Joule heating problem occurs for every electrical/electronic phenomena wherein current flow causes increase in temperature of the device. No heating elements are used and, in fact, the equivalent electrical circuit would depict the water itself as the resistive component.
In a conductor, the free electrons are always at random motion making collisions with ions or atoms of the conductor. The temperature change, delta_temp = (t x w) / (m x c) c for copper is 385 j per kg per.

Joule Heating Effect In Nonpolar And Bipolar Resistive Random Access Memory: Applied Physics Letters: Vol 107, No 7

Thermal Imaging Of The Joule Heating Inside The Structure And Cooling... | Download Scientific Diagram
![]()
Simulated Temperature Vs. Joule Heating Power Of Secondary Silicon... | Download Scientific Diagram

Effect Of Joule Heating On Transient Current And Electroluminescence In P-I-N Organic Light-Emitting Diodes Under Pulsed Voltage Operation - Sciencedirect